使用 OpenCV 解数独
寝室里一哥们申请出国,发了 N 封信,终于有人理他了,人家让他把做过的东西给他看看,他傻眼了,因为他的简历都是吹出来的!于是他找我和他一起干,做一个能解数独的安卓应用。他主要负责安卓应用开发,我负责 OpenCV 识别。其实我对 OpenCV 也只是知道一些皮毛,所以只好一边学一边做了。
首先,需要找一张数独的图,直接用了《编程之美》上 P.99 页的几张图。然后依次解决以下问题:
- 怎么在拍到的图中找到感兴趣的数独的区域
- 怎么从找到的区域中分离出每个数字,并知道每个数字的位置
- 怎么识别出不同的数字
一、找到数独所在区域
关于这个问题,想了几种方案,比如直线检测、矩形检测、连通域检测等等,最后用了最简单粗暴的方式:直接找面积最大的轮廓。
// 读取图像
Mat img, src;
src = imread(file, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
src.copyTo(img);
// 自适应二值化,中值滤波
adaptiveThreshold(img, img, 255, CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV, 25, 10);
medianBlur(img, img, 5);
// 遍历轮廓,找到面积最大的
vector< vector<Point> > contours;
findContours(img, contours, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
double area, maxArea = 100;
int maxIdx;
for(int i = 0; i != contours.size(); ++i) {
area = fabs(contourArea(contours[i]));
if(area > maxArea)
{
maxIdx = i;
maxArea = area;
}
}
// 对最大的轮廓做多边形近似,并判断是否符合要求
vector<Point> poly;
approxPolyDP(contours[maxIdx], poly, arcLength(contours[maxIdx], true) * 0.02, true);
if(poly.size() != 4 || fabs(contourArea(poly)) < 5000)
return false;
附图一张:
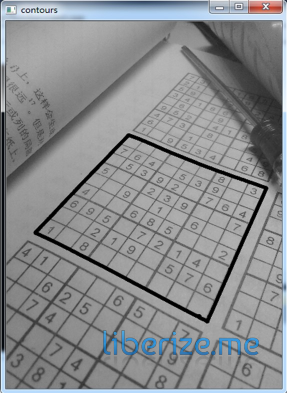
二、从数独区域分离出数字
考虑到得到的区域可能是不规则的四边形,先通过透视变换变成正方形。
// 将数独区域通过透视变换转为正方形
Mat dst(size, size, src.type()); // size 为目标边长,此处定为 303
// 首先确定轮廓中的四个点的对应位置
// 横纵坐标之和最小的认为是左上角的点,横纵坐标之差最大的认为是右上角的点
int sum, minSum = INT_MAX, ptTopLeft, dif, maxDif = INT_MIN, ptTopRight;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
sum = poly[i].x + poly[i].y;
dif = poly[i].x - poly[i].y;
if(sum < minSum) {
minSum = sum;
ptTopLeft = i;
}
if(dif > maxDif) {
maxDif = dif;
ptTopRight = i;
}
}
if(ptTopLeft != (ptTopRight+1)%4 && ptTopRight != (ptTopLeft+1)%4)
return false;
// 确定变换的四个源点和四个目标点
Point2f srcPoints[4] = {
Point2f(poly[ptTopLeft].x, poly[ptTopLeft].y),
Point2f(poly[ptTopRight].x, poly[ptTopRight].y),
Point2f(poly[(ptTopRight+2)%4].x, poly[(ptTopRight+2)%4].y),
Point2f(poly[(ptTopLeft+2)%4].x, poly[(ptTopLeft+2)%4].y)
},
dstPoints[4] = {
Point2f(0, 0),
Point2f(dst.cols-1, 0),
Point2f(0, dst.rows-1),
Point2f(dst.cols-1, dst.rows-1)
};
// 进行透视变换,并做边界补偿
Mat wrapMatrix = getPerspectiveTransform(srcPoints, dstPoints);
warpPerspective(src, dst, wrapMatrix, dst.size());
dst = dst(Rect(border, border, dst.cols-border*2, dst.rows-border*2));
附图一张:

完成以后,按行、列等间隔划分成 9x9 的小块,对每个小块切掉边界几个像素,然后去除面积小的区域,得到的就是背景全黑、只有数字的图像了。接着再找到包围数字的最小正方形,就可以做数字识别了。
adaptiveThreshold(dst, dst, 255, CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV, 25, 10);
int step = size/9; // step 为每个小方格的边长
Mat cell, num;
int result[81]; // result 用来存储识别结果
memset(result, 0, sizeof(result));
// 分割成 9x9 的图像分别进行处理
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
cell = dst(Rect(j*step+cut, i*step+cut, step-cut*2, step-cut*2));
// 去除面积小的区域
Mat img;
cell.copyTo(img);
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
findContours(img, contours, CV_RETR_LIST, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
Mat mask = Mat::zeros(cell.size(), cell.type());
for(int i = 0; i != contours.size(); ++i) {
if(fabs(contourArea(contours[i])) > areaThresh)
drawContours(mask, contours, i, Scalar(255), CV_FILLED);
}
for(int i = 0; i < cell.rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cell.cols; j++) {
if(mask.at<uchar>(i, j) == 0) {
cell.at<uchar>(i, j) = 0;
}
}
}
if(sum(cell)[0] == 0)
continue;
// 获得感兴趣区域
int left, right, top, bottom;
left = cell.cols;
right = 0;
top = cell.rows;
bottom = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < cell.rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cell.cols; j++) {
if(cell.at<uchar>(i, j) > 0) {
if(j < left) left = j;
if(j > right) right = j;
if(i < top) top = i;
if(i > bottom) bottom = i;
}
}
}
int width = right - left;
int height = bottom - top;
int len = (width < height) ? height : width;
num = Mat::zeros(len, len, CV_8UC1);
Rect dstRect((len - width)/2, (len - height)/2, width, height);
Rect srcRect(left, top, width, height);
Mat dstROI = num(dstRect);
Mat srcROI = cell(srcRect);
srcROI.copyTo(dstROI);
// 识别数字
result[i*9+j] = recNum(num);
}
// 打印识别结果
for(int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
cout << result[i*9+k] << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
继续上图:
三、识别不同数字
此处使用支持向量机(SVM)来做数字识别。将上一步得到的 ROI 缩放成 sampleSize*sampleSize 大小,然后转成向量,就可以根据实现训练好的数据进行识别了。
至于训练过程,其实也不难,自己做 1000 多个样本,然后人工识别了一下,写一个训练的程序,每次读入样本和识别结果进行训练就可以了。
CvSVM svm = CvSVM();
svm.load( "../SVM_DATA.xml" );
int recNum(const Mat &num)
{
Mat temp = Mat::zeros(sampleSize, sampleSize, CV_8UC1);
Mat data = Mat::zeros(1, sampleSize*sampleSize, CV_32FC1);
// 统一大小
resize(num, temp, temp.size());
// 转成向量
for(int i = 0; i < sampleSize; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < sampleSize; j++) {
data.at<float>(0, i*sampleSize+j) = temp.at<uchar>(i, j);
}
}
// 归一化、预测
normalize(data, data);
return char(svm.predict(data)) - '0';
}
完整代码见 Gist:https://gist.github.com/liberize/7526824。本文中为了查看方便,修改了代码结构,但思路是一样的。训练的代码见 Gist:https://gist.github.com/liberize/7526893。其中样本是按 0.png, 1.png ... 进行编号的存放在 sample 目录下,每个样本对应的标签是按样本编号 标签格式按行存放在 label.txt 文件中。